
CNC machining plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, providing the precision and control needed to produce components consistently and efficiently. It is especially valuable for applications that demand tight tolerances, repeatable cuts, and high-quality finishes, all of which support reliable production outcomes.
However, even advanced CNC systems can fall short if operators do not fully understand how they function. Improper programming, incorrect setup, or inadequate tool handling can lead to scrap, workflow interruptions, and delays that affect equipment uptime and overall productivity.
To help you avoid these challenges, this guide explains what machining CNC is and how it works, highlighting practices that enhance accuracy, consistency, and efficiency throughout your production process.
Key Takeaways
CNC machining ensures precise, consistent, and high-quality parts, reducing scrap and rework.
Automation delivers faster production, better throughput, and less reliance on operator skill compared with manual machining.
Success depends on proper CAD/CAM programming, machine setup, tooling, and human oversight for quality.
Choosing the right CNC machine and integrating it strategically into operations maximizes efficiency, scalability, and ROI.
Industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and industrial equipment benefit from CNC’s precision, repeatability, and operational consistency.
Machining CNC: Driving Consistency and Control
CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, uses software to guide cutting tools and move workpieces automatically. Instead of relying on manual adjustments, you program the machine with instructions generated from CAD designs.
This method reduces errors, ensures precise results, and maintains consistency across every batch.
By using CNC, you can reliably produce complex parts while keeping production predictable and efficient.
CNC vs. Manual Machining: Key Operational Difference
Making the right choice between machining CNC and manual machining affects production efficiency, cost per unit, and quality. Here is a strategic comparison:
Operational Factor | Machining CNC | Manual Machining | Strategic Impact |
Control and Accuracy | Fully automated through software | Dependent on operator skill | CNC ensures repeatable precision, reducing errors and rework |
Production Consistency | Identical parts every batch | Variable output | Supports stable throughput and predictable lead times |
Speed and Throughput | Can operate continuously | Limited by operator fatigue | Accelerates delivery and improves capacity utilization |
Complex Part Capability | Multi-axis and complex geometries | Limited to simple shapes | Enables advanced designs and reduces multiple setups |
Labor and Resource Efficiency | Less hands-on, operators focus on supervision | Operator required for all steps | Frees skilled staff and lowers labor cost |
Scalability and Flexibility | Easy to scale from prototype to mass production | Scaling increases labor and variation | Supports growth and quick response to demand changes |
Quality Assurance | Minimal variation, consistent output | Frequent inspections required | Enhances yield, reduces scrap, and ensures process reliability |
And why machining CNC should be part of your production strategy:
Integrating CNC machining into your operations helps you maintain quality, reduce waste, and optimize production flow.
You can scale efficiently from prototype to full production, reduce reliance on manual labor, and achieve predictable results across every batch.
Machining CNC keeps production predictable because the machine follows programmed designs rather than manual adjustments, which means each cut matches the last and quality stays steady through long shifts and large batches.
To make that level of consistency practical on the shop floor, Cutting Edge Plasma provides CNC systems like the iPlasma XTREME 5100 CNC Plasma Table, Lockwood PRO 5100 CNC Router are built to maintain stable motion, clean cutting paths, and uninterrupted throughput.
So the precision delivered by machining CNC translates directly into fewer errors, faster turnaround, and reliable batch-to-batch quality as production scales.
How CNC Machining Works: From Design to Finished Part
CNC machining follows a structured workflow that integrates design, programming, and automated operation. Understanding this process helps plant managers and operations leaders evaluate efficiency and output consistency.
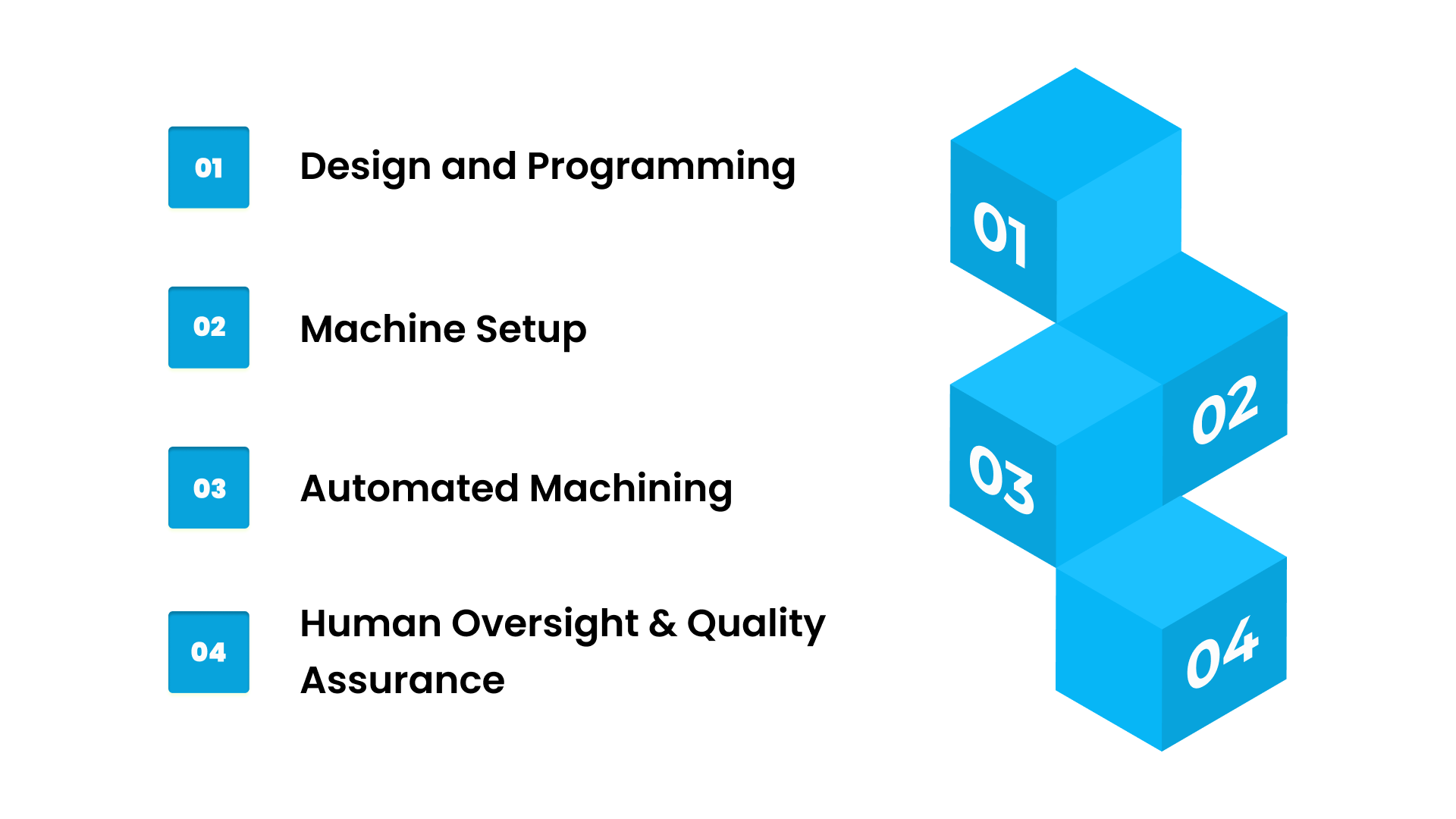
1. Design and Programming
The process starts with creating a 3D model using CAD software. CAM software then converts the design into a CNC-readable program, usually in G-code. This program defines the movement of the machine’s tools and the operation sequence.
2. Machine Setup
Correct tooling is selected, stock material is loaded, fixtures are mounted, and the machine is calibrated. Proper setup ensures minimal errors during production and supports consistent quality.
3. Automated Machining
CNC machines execute the program to perform cutting, milling, turning, drilling, or other operations automatically. Tool changes, spindle speed adjustments, and feed rates are controlled digitally to maintain precision.
4. Human Oversight and Quality Assurance
Operators monitor the process, handle material loading and unloading, and inspect outputs to ensure quality standards are met. Human oversight complements automation, ensuring production runs efficiently and safely.
This workflow allows manufacturers to reliably produce identical parts, reducing scrap and supporting both rapid prototyping and scaled production.
4 Key CNC Machine Types for Every Production Need
Selecting the right CNC machine for your operations is critical to achieve cost-effectiveness. Each type of machine has specific strengths that suit different production goals, materials, and part complexities.
Understanding these options helps you make informed decisions and optimize workflow.
1. CNC Milling Machines
Milling machines are ideal when you need to produce parts with complex, multi-axis geometries. Their versatility allows you to handle intricate shapes, pockets, and contours, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial components.
Using milling machines helps you maintain consistent quality while supporting varied production requirements.
2. CNC Lathes (Turning Centers)
Lathes are designed to produce rotational or symmetrical parts such as shafts, bushings, and cylindrical housings. Automating the turning process ensures high consistency, faster production, and reduced errors compared with traditional manual lathes.
3. CNC Laser, Plasma, and Water-Jet Cutters
These cutting machines excel at shaping sheet materials and creating precise 2D profiles. If your parts require accuracy and fast turnaround, these machines provide clean, repeatable cuts while minimizing material waste.
4. 3-Axis to 5-Axis CNC Machines
Multi-axis machines offer advanced capabilities for producing complex geometries in a single setup. By reducing the need for multiple setups, they save time, improve precision, and increase overall operational efficiency for high-complexity parts.
Understanding which CNC machine aligns with your production needs allows you to optimize throughput, improve machine utilization, and lower per-unit costs, ensuring your operations remain competitive and efficient.
How to Get Started with CNC Machining?
Integrating CNC machining into your operations requires careful planning to maximize efficiency and ensure consistent results. Consider the following steps to set up a successful CNC workflow:
1. Adopt CAD and CAM Software
Equip your design and engineering teams with software that generates CNC-ready programs efficiently, ensuring designs translate accurately to machine instructions.
2. Machine Setup and Maintenance
Properly calibrate your machines, design fixtures for stability, and follow preventive maintenance routines to maintain precision, avoid unexpected downtime, and extend equipment life.
3. Tooling and Material Selection
Select tooling and stock materials that match the parts you intend to manufacture. Correct pairing of tools and materials improves cutting efficiency, reduces scrap, and ensures higher-quality parts.
4. Automation and Staff Training
Invest in training for operators to program, monitor, and maintain CNC machines. Skilled personnel help optimize productivity, maintain consistent output, and minimize errors or downtime.
5. Quality Assurance and Monitoring
Implement regular inspections, process monitoring, and data logging to detect deviations early. This approach lowers scrap rates and keeps production consistent and reliable.
6. Production Volume and Mix Planning
Plan your CNC workflow according to your production goals. Whether handling prototypes or large-scale runs, aligning machine selection and operational processes with your volume requirements ensures smoother operations and predictable outcomes.
By addressing these considerations thoughtfully, you can integrate CNC machining effectively into your operations, reduce errors, and maintain steady, high-quality production.
5 Essential Considerations for CNC Integration
CNC machining can enhance your operations by simplifying workflows and maintaining reliable production quality. However, to make the most of these benefits, it’s important to be aware of the operational realities that can affect performance.
Understanding these factors helps you plan effectively, avoid common pitfalls, and maximize efficiency.
While CNC machining offers substantial benefits, some operational realities must be addressed:
Initial Investment: You’ll need to allocate funds for machines, software, tooling, and training, but this upfront cost pays off through consistent quality, reduced errors, and improved production efficiency over time.
Setup and Programming: Ensuring your CNC machine is correctly programmed and set up is critical. Accurate setups prevent mistakes, reduce rework, and keep operations running smoothly.
Maintenance and Calibration: Regular maintenance and calibration help you maintain precision, prevent unexpected downtime, and extend the life of both tools and equipment.
Tool and Material Compatibility: Choosing the right tools for each material ensures clean cuts, protects your machines, and keeps production efficient without compromising part quality.
Quality Control: Even with automation, you need to monitor output and follow inspection protocols to ensure every part meets your design specifications and industry standards.
Recognizing these considerations ensures smooth operations and maximizes the benefits of CNC adoption.
5 Strategic Industry Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining helps you achieve consistent results and efficiency across industries that demand precision and reliability. By automating cutting, shaping, and drilling, it ensures high-quality output while reducing errors and downtime.
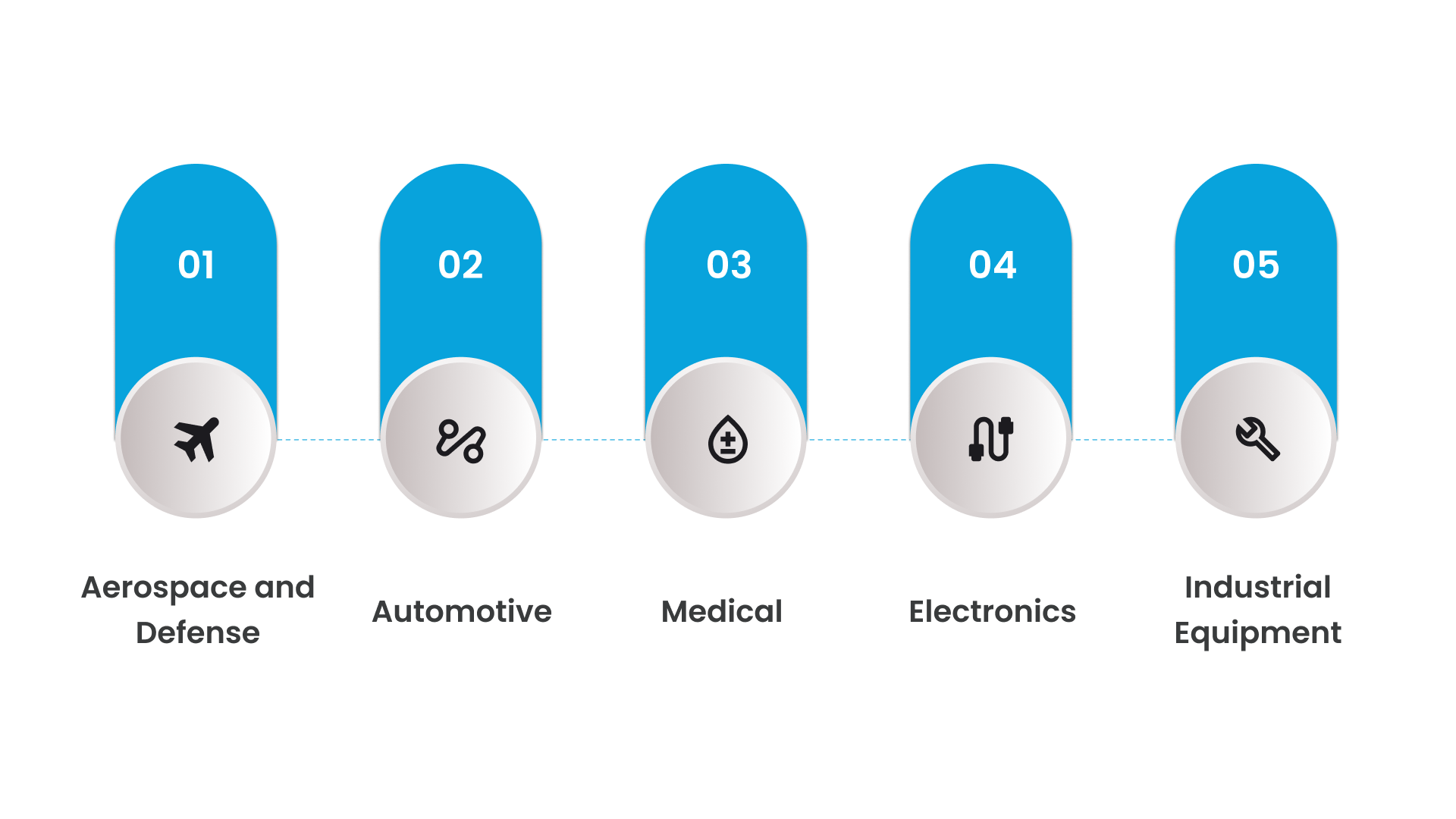
Here’s how you can use CNC machining in different sectors:
1. Aerospace and Defense
You can rely on CNC machines to produce structural components, hydraulic fittings, and engine parts with exact dimensions. This ensures safety, uniform performance, and compliance with strict industry standards.
2. Automotive
Using CNC machining, you can create engine components, transmission housings, and precision shafts with consistent quality. Automation reduces rework, minimizes mistakes, and streamlines assembly processes for smoother operations.
3. Medical
You can produce surgical tools, implants, and prosthetics with the accuracy required for critical applications. CNC machining lets you create complex geometries while ensuring repeatable results and supporting patient safety.
4. Electronics
CNC systems help you manufacture small but essential parts like housings, connectors, and heat sinks with exact tolerances. This ensures reliable performance and reduces failures in your electronic assemblies.
5. Industrial Equipment and Machinery
You can make shafts, gears, hydraulic components, and tooling fixtures that meet high-quality standards. Consistent machining improves equipment performance, reduces maintenance, and supports your operational goals.
Why This Matters for Your Operations:
By using CNC machining, you can reduce scrap, maintain predictable production schedules, and scale efficiently. Systems from Cutting Edge Plasma provide multi-axis control, stable tooling, and real-time monitoring to help you maintain precision, improve throughput, and operate efficiently.
CNC machining gives you the tools to meet high-demand requirements while keeping quality, safety, and efficiency at the forefront of your operations.
Why Choose Cutting Edge Plasma for CNC Machining Excellence?
Precision, reliability, and efficiency are essential for modern manufacturing. Our Cutting Edge Plasma CNC systems are built to deliver consistent, high-quality parts while keeping operations safe and streamlined.
With advanced features designed to reduce errors and simplify complex tasks, our machines help you maintain smooth production and dependable results every time.
Here’s how we support smoother CNC machining and stronger operational results:
1. Precise Multi-Axis Control
Our plasma systems allow accurate movement across multiple axes, enabling complex part geometries and consistent quality. This capability reduces rework, improves yield, and ensures repeatable results for every production run.
2. Stable Fixturing and Tooling
Robust fixtures and optimized tooling minimize vibration and part movement during cutting. This ensures dimensional accuracy, protects tools, and delivers consistent results across batches.
3. Intuitive Control Interface
Operators can easily adjust feed rates, cutting speed, and tool paths with a user-friendly interface. Simplified programming reduces setup errors, accelerates workflow, and ensures consistent output.
4. Integrated Monitoring and Safety Systems
Real-time machine monitoring tracks performance and alerts operators to potential issues. Safety features reduce the risk of accidents, minimize downtime, and maintain stable production.
5. Ongoing Support and Service
We provide dedicated technical support and guidance to optimize machine performance. With warranty coverage and service programs, you can operate with confidence and keep production running smoothly.
Choosing Cutting Edge Plasma helps you streamline CNC machining, maintain part consistency, and reduce manual intervention.
Features like multi-axis precision, secure fixturing, intuitive control, real-time monitoring, and dedicated support allow you to optimize KPIs such as throughput, yield, and equipment uptime while achieving high-quality results consistently.
Conclusion
Using a CNC machine properly protects your equipment, ensures precise parts, and keeps operations running smoothly. By preparing materials carefully, choosing the right tools, and operating the machine correctly, you reduce errors, maintain consistent quality, and extend machine life.
With Cutting Edge Plasma, features like accurate multi-axis control, stable fixtures, and an intuitive interface make achieving reliable results easier.
Contact Cutting Edge Plasma today to explore our machines, tools, and expert guidance for efficient, precise CNC operations.
FAQs
1. Is CNC machining suitable for complex or precision parts?
Yes. CNC machines can produce intricate geometries and multi-axis components with high precision and repeatable quality, making them ideal for both prototypes and full-scale production runs.
2. How do I reduce scrap and improve part consistency?
Accurate programming, proper machine setup, and regular maintenance are key. Using the right tooling for the material and monitoring operations ensures minimal variation and lowers scrap rates.
3. Which CNC machine is best for beginners or small-scale operations?
A 3-axis CNC milling machine or a simple CNC lathe is ideal for smaller setups. These machines are easier to program, operate, and maintain while still delivering precise results.
4. When should tooling or machine components be replaced?
Inspect tools and wear-prone parts regularly. Replace any worn, chipped, or damaged tooling to maintain precision, reduce downtime, and protect your machine.
5. How can CNC operations be managed safely?
Ensure operators are trained, wear appropriate protective gear, and follow standard operating procedures. Maintain clean workspaces, secure materials properly, and monitor automated processes to prevent accidents.


